: Home » Blog » Mining Industry News » The Impact of Geology on Mining Techniques
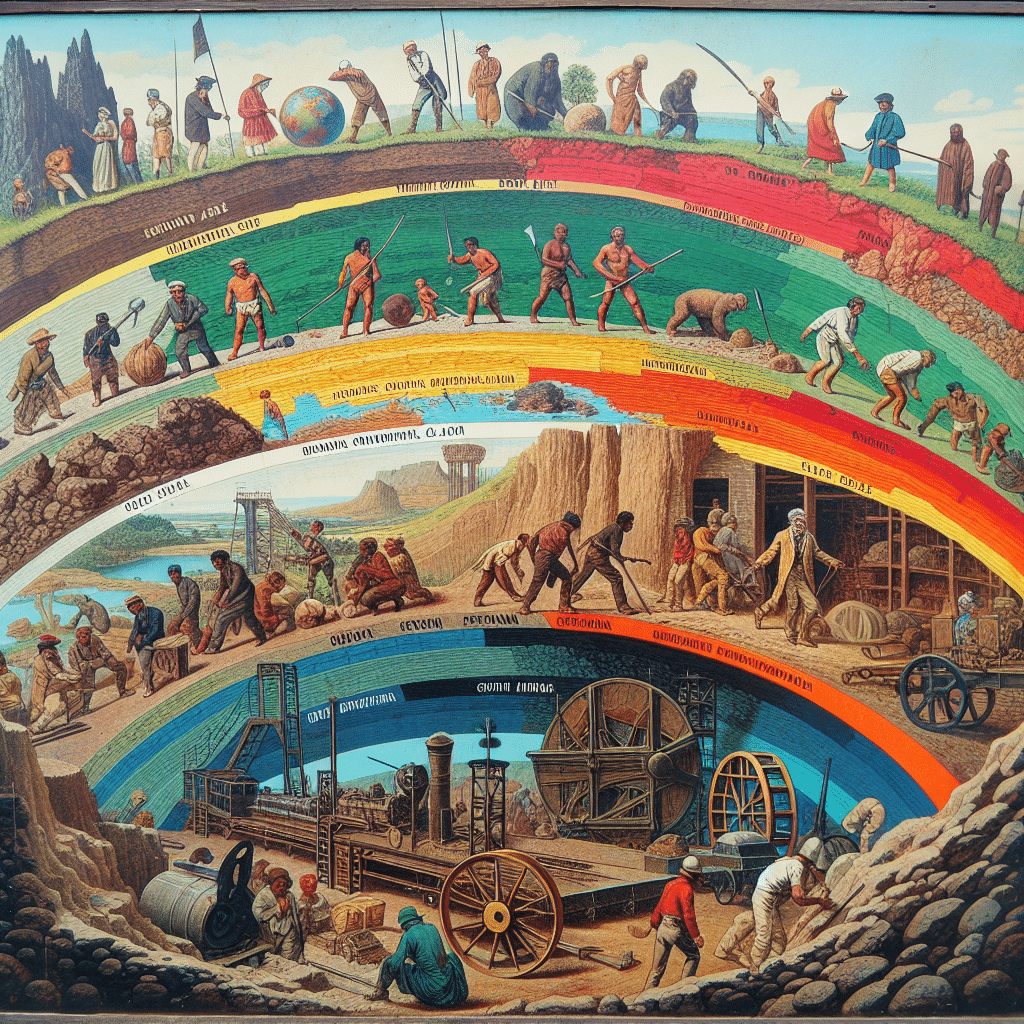
Geology and mining history have always been closely intertwined. The study of geology is crucial for understanding the earth’s composition and structure, which in turn affects the techniques used in mining. In this article, we will explore the impact of geology on mining techniques and how advancements in geology have revolutionized the mining industry.
Geology plays a significant role in determining the location and accessibility of mineral deposits. Different types of rocks and minerals are found in specific geological formations, and understanding these formations is essential for successful mining operations. For example, certain minerals may be concentrated in sedimentary rocks, while others may be found in igneous or metamorphic rocks. By studying the geology of an area, miners can identify potential mineral deposits and plan their mining operations accordingly.
One of the key factors that geology influences in mining techniques is the type of mining method used. There are several mining methods, including open-pit mining, underground mining, and placer mining. The choice of method depends on various geological factors, such as the depth and shape of the deposit, the type of rock, and the presence of water. For instance, open-pit mining is suitable for shallow deposits that are close to the surface, while underground mining is used for deeper deposits.
Geological surveys and mapping are crucial for determining the feasibility of mining operations. These surveys help identify the size, shape, and quality of mineral deposits, as well as any potential geological hazards. By analyzing the geological data, miners can assess the economic viability of a mining project and make informed decisions about resource extraction.
Advancements in geology have greatly improved mining techniques over the years. With the development of technologies such as remote sensing, satellite imagery, and geophysical surveys, geologists can now gather detailed information about the earth’s subsurface without physically accessing the site. This allows for more accurate mapping of mineral deposits and better planning of mining operations.
Geological modeling is another area where advancements in geology have had a significant impact on mining techniques. By creating three-dimensional models of the subsurface, geologists can visualize the distribution of minerals and predict their behavior during mining operations. This helps optimize the extraction process and minimize waste.
Geological knowledge also plays a crucial role in environmental management in mining. By understanding the geology of an area, miners can assess the potential impact of mining activities on the surrounding environment. They can identify sensitive ecosystems, water sources, and geological features that need to be protected. This knowledge allows for the implementation of sustainable mining practices that minimize environmental damage.
In conclusion, geology has a profound impact on mining techniques. The study of geology helps identify mineral deposits, determine the most suitable mining method, and assess the feasibility of mining projects. Advancements in geology have revolutionized the mining industry, allowing for more accurate mapping, better planning, and sustainable mining practices. By understanding the geological aspects of mining, we can ensure the responsible extraction of Earth’s valuable resources while minimizing environmental impact.
Mining has played a significant role in shaping the history and development of Arizona. From the early days of prospecting to the boom of the mining industry, the region’s geology has been a driving force behind its economic growth. In this article, we will explore the rich history of mining in Arizona and how it has shaped the landscape and the lives of its inhabitants.
The geological composition of Arizona is diverse and abundant in mineral resources. The region is known for its rich deposits of gold, silver, copper, and other valuable minerals. These resources have attracted prospectors and miners from all over the world, seeking their fortunes in the rugged terrain.
The history of mining in Arizona can be traced back to the early 19th century when the first explorers ventured into the area in search of gold. These early prospectors faced numerous challenges, including harsh weather conditions, rugged landscapes, and limited infrastructure. However, their perseverance paid off, and soon, gold mines began to spring up across the region.
As the mining industry grew, so did the population of the black hills. Towns and settlements were established near the mines, providing essential services and support to the miners. These towns became vibrant communities, with schools, churches, and businesses catering to the needs of the growing population.
The mining boom in Arizona reached its peak in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. During this time, the region was one of the largest producers of gold in the country. The mining industry provided employment opportunities for thousands of people, attracting workers from all walks of life.
However, the mining industry also had its dark side. The harsh working conditions and lack of safety regulations led to numerous accidents and fatalities. Miners faced the constant danger of cave-ins, explosions, and exposure to harmful gases. Despite these risks, many miners continued to work in the mines, driven by the promise of wealth and a better life.
Over time, the mining industry in Arizona began to decline. Depletion of resources, changing market conditions, and the rise of alternative energy sources contributed to the decline of the industry. Many mines were closed, and the once-thriving towns became ghost towns, with only remnants of their former glory.
Today, the mining industry in Arizona is a shadow of its former self. However, the rich history of mining is still evident in the landscape and the stories of the people who once worked in the mines. Many abandoned mines have been preserved as historical sites, offering visitors a glimpse into the region’s mining past.
In conclusion, the history of mining in Arizona is a testament to the resilience and determination of the people who shaped the region’s development. The rich geological composition of the area attracted prospectors and miners, leading to a mining boom that transformed the landscape and the lives of its inhabitants. While the mining industry has declined in recent years, the legacy of mining in Arizona lives on, reminding us of the challenges and triumphs of those who came before us.

Geology and mining history go hand in hand, as the geological factors of an area often determine the presence and abundance of valuable minerals. These minerals, in turn, attract miners and shape the development of mining communities. In this article, we will explore the fascinating relationship between geology and mining history, and how the geological features of an area can leave a lasting impact on the communities that spring up around mining operations.
One of the key geological factors that shape mining communities is the presence of mineral deposits. Certain types of rocks and formations are more likely to contain valuable minerals, such as gold, silver, copper, or coal. When these deposits are discovered, it can lead to a rush of miners flocking to the area in search of fortune. This influx of people often leads to the rapid growth of a mining community, with new businesses, housing, and infrastructure being built to support the growing population.
The geology of an area also plays a role in determining the methods and techniques used in mining operations. For example, the type of rock or soil can affect the ease of extracting minerals. Soft, easily erodible materials may require less intensive mining techniques, while harder materials may require more advanced machinery and drilling methods. The geology of an area can also impact the safety of mining operations, as unstable rock formations or the presence of underground water can pose significant risks to miners.
In addition to the physical aspects of geology, the history of mining in an area can also shape the development of mining communities. Many mining towns have a rich heritage and a strong sense of identity tied to their mining history. The stories of the miners who toiled underground, the struggles they faced, and the triumphs they achieved are often passed down through generations, creating a deep connection to the land and the industry.
Mining history can also leave a lasting impact on the landscape. Open-pit mines, for example, can result in large scars on the earth’s surface, altering the natural topography of an area. These scars can be seen as both a reminder of the past and a symbol of the economic importance of mining to the community. In some cases, old mining sites have been repurposed for other uses, such as recreational areas or tourist attractions, preserving the history of the area while providing new opportunities for the community.
The relationship between geology and mining history is a complex one, with each influencing and shaping the other. The geological factors of an area determine the presence and abundance of minerals, which in turn attract miners and shape the development of mining communities. The methods and techniques used in mining operations are also influenced by the geology of an area, as well as the safety considerations. The history of mining in an area creates a sense of identity and heritage for mining communities, and can leave a lasting impact on the landscape.
In conclusion, geology and mining history are deeply intertwined, with the geological factors of an area playing a crucial role in shaping mining communities. From the presence of mineral deposits to the methods used in mining operations, geology influences every aspect of the mining industry. The history of mining in an area further adds to the unique character of mining communities, leaving a lasting impact on the landscape and the people who call these places home.
Mining has been an integral part of human civilization for thousands of years. From the early days of using simple tools like pickaxes to the modern machinery we have today, the evolution of mining technology has been a fascinating journey. In this article, we will explore how mining technology has evolved over time and the impact it has had on the industry.
In ancient times, mining was a labor-intensive process that relied heavily on human strength and basic tools. Miners would use pickaxes to break through rocks and extract valuable minerals. This method was slow and inefficient, requiring a great deal of physical effort. However, it was the only option available at the time, and it allowed civilizations to access the resources they needed for survival and development.
As time went on, advancements in technology began to revolutionize the mining industry. The Industrial Revolution in the 18th century brought about significant changes, with the invention of steam-powered machinery. Steam engines were used to power pumps that could remove water from mines, allowing for deeper and more extensive mining operations. This innovation greatly increased the efficiency and productivity of mining, making it possible to extract larger quantities of minerals in a shorter amount of time.
The 19th century saw further advancements in mining technology with the introduction of dynamite. This explosive material made it easier to break through hard rock and access previously inaccessible mineral deposits. It also led to the development of underground mining techniques, as miners could now safely excavate tunnels and shafts to reach deeper deposits.
The 20th century brought even more significant changes to the mining industry. The invention of electricity and the development of diesel engines allowed for the creation of more powerful and efficient mining machinery. Electric-powered drills and loaders replaced manual labor, making the extraction process faster and safer. This not only increased productivity but also improved the working conditions for miners.
In recent decades, the mining industry has witnessed a technological revolution with the introduction of computerized systems and automation. Modern mining machinery is equipped with advanced sensors and control systems that allow for precise and efficient operations. These machines can be remotely controlled and monitored, reducing the risk to human operators and increasing overall safety.
Furthermore, the use of data analytics and artificial intelligence has revolutionized the way mining operations are managed. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize production, predict equipment failures, and improve resource management. This level of automation and intelligence has transformed the mining industry, making it more efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly.
In conclusion, the evolution of mining technology from pickaxes to modern machinery has been a remarkable journey. From the labor-intensive methods of ancient times to the highly automated and sophisticated systems we have today, mining has come a long way. These advancements have not only increased productivity and efficiency but have also improved the safety and sustainability of the industry. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations that will shape the future of mining and ensure its continued importance in our modern world.
Mining has been an integral part of human civilization for centuries. From the early days of digging for precious metals to the modern extraction of minerals, mining has shaped our world in many ways. However, along with its benefits, mining has also had significant environmental impacts. In this article, we will explore the past, present, and future environmental impacts of mining.
In the past, mining practices were often unregulated and had devastating consequences for the environment. The extraction of minerals required the removal of large amounts of earth, leading to deforestation and habitat destruction. Additionally, the use of toxic chemicals, such as mercury and cyanide, in the extraction process resulted in water pollution and the contamination of surrounding ecosystems. These practices had long-lasting effects on the environment, with some areas still struggling to recover from the damage caused by historical mining activities.
Fortunately, awareness of the environmental impacts of mining has grown over time, leading to the implementation of regulations and best practices. Today, mining companies are required to adhere to strict environmental standards and mitigate the negative effects of their operations. For example, they must develop comprehensive reclamation plans to restore mined areas to their original state once mining activities are complete. This includes reestablishing vegetation, controlling erosion, and ensuring the long-term stability of the land.
Despite these improvements, mining still poses significant environmental challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the generation of large amounts of waste, known as tailings. These tailings often contain toxic substances and can pose a threat to nearby water sources if not properly managed. Additionally, the extraction of minerals requires the use of energy, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. As the demand for minerals continues to grow, it is crucial to find sustainable solutions to minimize these impacts.
Looking to the future, advancements in technology and a shift towards sustainable mining practices offer hope for reducing the environmental impacts of mining. For instance, the development of cleaner extraction methods, such as bioleaching and phytomining, can minimize the use of harmful chemicals and reduce water pollution. Furthermore, the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can help reduce the carbon footprint of mining operations.
In addition to technological advancements, collaboration between mining companies, governments, and local communities is essential for addressing the environmental impacts of mining. By working together, stakeholders can develop strategies to protect ecosystems, conserve biodiversity, and ensure the sustainable use of natural resources. This includes engaging in dialogue with indigenous communities, who often have a deep understanding of the land and can provide valuable insights into sustainable mining practices.
In conclusion, mining has had a significant impact on the environment throughout history. While past mining practices were often destructive, there has been progress in mitigating the negative effects of mining through regulations and best practices. However, challenges still remain, such as waste management and greenhouse gas emissions. By embracing technological advancements and fostering collaboration, we can work towards a future where mining is conducted in a sustainable and environmentally responsible manner.